SKEDSOFT
Introduction:
For selecting a gearbox, its structure type, installation form, bearing capacity, output rotational speed, working conditions and other factors shall be considered.
Types of the gear box:
(a) Selective type gear boxes:
(i) Sliding mesh gear box
(ii) Constant mesh gear box
(iii) Synchromesh gear box
(b) Progressive type gear box
(c) Epicyclic type gear box.
Sliding Mesh Gear Box: 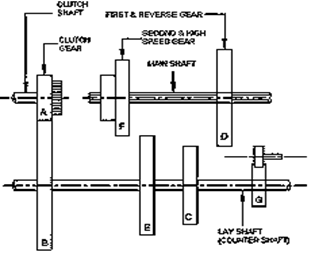
- It is simplest type of gear box out of the available gear boxes.
- In this type of gear box, gears are changed by sliding one gear on the other.
- This gear box consists of three shafts; main shaft, clutch shaft and a counter shaft.
- In a four speed gear box (which includes one reverse gear), the counter shaft has four gears which are rigidly connected to it.
- Clutch shaft has one gear and main shaft has two gears.
- The two gears on the main shaft can slide in the horizontal direction along the splines of the main shaft.
- However, the gears on the counter shaft cannot slide. The clutch gear is rigidly fixed to the clutch shaft. It is always connected to the countershaft drive gear.
Constant Mesh Gear Box:
- In this gear box, all gears on the main transmission shaft are constantly connected to corresponding gears on countershaft or lay shaft.
- In addition, two dog clutches are provided on the main shaft.
- One dog clutch is between the second gear and cutch gear and another is between the first gear and reverse gear.
- Splines are out on main shaft so that all the gears are feed on it.
- Dog clutches can also slide on main shaft and rotate with it. However, all the gears on countershaft are giddily fixed to it.
- Different gear ratios (speed ratios) are obtained as follows :
- For Three Forward and One Reverse Gear
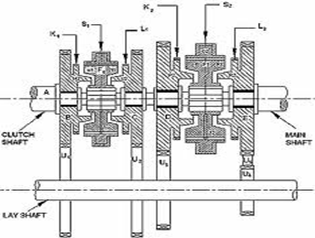
- Top or 3rd speed gar is obtained when the left dog clutch is slided to left to mesh with clutch gear by using the gear shift lever. In this case, main shaft rotates at the same speed as that of clutch gear or engine crankshaft speed which is the maximum speed. Speed ratio obtained is 1: 1.
- Second gear is obtained when dog cutch (left side) meshes with second gear. In this condition clutch gear rotates the drive gear on countershaft and countershaft drives the second gear on the main shaft. All other gears on main shaft are free, so they do not move.
- In the same manner, first gear is obtained when right hand side dog clutch meshes with first gear. Reverse gear is obtained when right side dog clutch meshes with reverse gear on main shaft.