SKEDSOFT
Introduction:
TQM tools and techniques are the ON-LINE methods of finding out if customer requirements are met both internally and externally. Tools and techniques are therefore the sensors which can be used in every process of business to establish the standard of quality at each stage of each process by ensuring that there is total compliance with customer requirements.
Ways of using tools and techniques:
Tools and techniques can be used in two different ways:
(i) Reactive role: A problem has been identified and a process seeking to solve it is carried out;
(ii) Proactive role: The continuous search for improvement by isolating possible bottlenecks and seeking to solve them through a process using TQM tools and techniques.
TQM places much emphasis on continuous improvement. ON-LINE problem solving is therefore essential if superior performance is to be achieved. Once a culture of problem-solving activity is established, it is therefore expected that a proactive approach rather than a reactive one will take place.
Stages of problem solving activity:
The process of solving problems using TQM tools and techniques has to go through various important stages which should include the following:
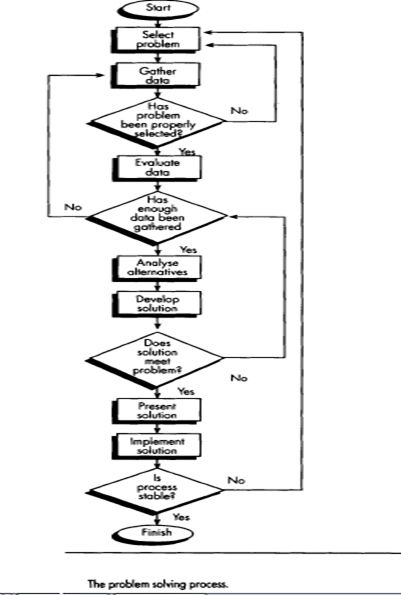
- Problem selection:It is vital that the right problem is selected, i.e. the one which causes most concern and not one that we have imagined. It is therefore important in the problem solving process, to ask very much earlier on, whether the right problem has been selected.
- Data gathering:This is a very important aspect. Enough data has to be collected using various means. The data has to include various aspects of the business and should not just be confined to the process under scrutiny itself. It may be that the solution to the problem lies in some peripheral aspects of the business, which under normal circumstances, would not have been considered to be important.
- Fact evaluation:This is a stage which intends to quantify the various data collected and its appropriateness to the problem being considered. It is also a stage where it can be decided whether more data ought to be collected.
- Data analysis: This stage tries to relate each piece of data collected to one aspect of the problem and basically tries to put the jigsaw together. It ponders over each solution, its potential, limitations, and consequences on other activities and so on.
- Solution development:The most effective, practical, economically viable solution is selected, discussed and presented to management.
- Solution implementation:The implemented solution has to be monitored and controlled. If further hidden problems have been isolated linked to the same process, then review of the problem selected and data gathered, has to take place. If the solution has been implemented successfully and the process is stable, the problem-solving activity can be moved to another area.